Algorithm to Check if All Points are On the Same Line
- Time:2020-09-09 13:16:32
- Class:Weblog
- Read:49
You are given an array coordinates, coordinates[i] = [x, y], where [x, y] represents the coordinate of a point. Check if these points make a straight line in the XY plane.
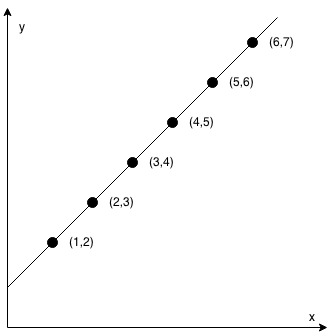
Input: coordinates = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[6,7]]
Output: true
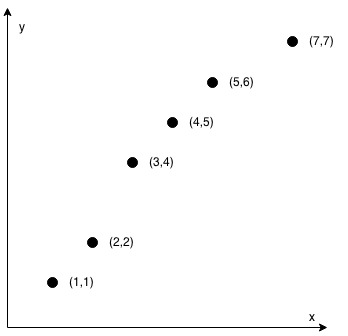
Input: coordinates = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[7,7]]
Output: false
Constraints:
2 <= coordinates.length <= 1000
coordinates[i].length == 2
-10^4 <= coordinates[i][0], coordinates[i][1] <= 10^4
coordinates contains no duplicate point.Hints:
If there’re only 2 points, return true.
Check if all other points lie on the line defined by the first 2 points.
Use cross product to check collinearity.
Cross Product to Check If Points are On a Line
If there are less than or equal to two points, we return true – as 1 or 2 points must be on the line. Then we use the first two points to compute the delta x and y offsets. Then checking from the third point, we can use the cross product to see if it is the same.
The following C++ implementation has O(N) linear runtime complexity.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | class Solution { public: bool checkStraightLine(vector<vector<int>>& coordinates) { if (coordinates.size() <= 2) return true; int dx = coordinates[0][0] - coordinates[1][0]; int dy = coordinates[0][1] - coordinates[1][1]; for (int i = 2; i < coordinates.size(); ++ i) { int dx1 = coordinates[0][0] - coordinates[i][0]; int dy1 = coordinates[0][1] - coordinates[i][1]; if (dx1 * dy != dy1 * dx) return false; } return true; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
bool checkStraightLine(vector<vector<int>>& coordinates) {
if (coordinates.size() <= 2) return true;
int dx = coordinates[0][0] - coordinates[1][0];
int dy = coordinates[0][1] - coordinates[1][1];
for (int i = 2; i < coordinates.size(); ++ i) {
int dx1 = coordinates[0][0] - coordinates[i][0];
int dy1 = coordinates[0][1] - coordinates[i][1];
if (dx1 * dy != dy1 * dx) return false;
}
return true;
}
};The cross product (one of the most classic geometrygeometry algorithms) returns the perpendicular vector/line to the original line. If the cross product is the same, then the point must be on the same line.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
Recommend:Summits set epoch-making milestone in history of China-Arab ties
In the face of COVID-19 pandemic, China and Arab countries have
15 Macao residents qualify as candidates for deputies to nationa
Study finds genetic solution to pre-harvest sprouting in rice, w
Bodybuilders dying as coaches, judges encourage extreme measures
Malta's Marsaskala, China's Dujiangyan sign sister city agreemen
U.S. mortgage applications continue slide amid surging interest
Russian, UAE presidents discuss bilateral cooperation over phone
Hate crimes in U.S. Los Angeles County rise to highest level sin
Chinese mainland reports 4,031 new local confirmed COVID-19 case
- Comment list
-
- Comment add